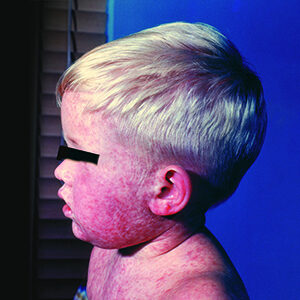
SRHD Works to Bring Health Equity to Vaccination Messaging
Recognizing the need to bring health messaging to the community in various languages, SRHD Immunization Assessment & Promotion program developed culturally competent, ethnically diverse fliers and posters in multiple languages that promote routine childhood immunizations.